Welcome to the Master's degree program Computational Science and Engineering.
Detailed information on the program according to SPSO from 2018 can be found on this page.
On the web pages of the university you will find a brief overview of general information and information about admission and enrollment.
The enrollment-specific examination and study regulations (SPSO) of 2018 – in connection with the current version of the Framework Examination Regulations for the Bachelor and Master Courses of the University of Rostock (RPO BSc / MSc) – are the basis for the enrollment in this course of studies.
For modules of foreign faculties that are enrolled in the elective area, the respective SPSOs of the faculties offering the modules, in which these modules are anchored, apply. For the language modules that can be studied in the compulsory elective course, the examination regulations apply to the courses offered by the Language Center of the University of Rostock, including the university foreign language certificate UNIcert®.
The CSE course is offered in English and is therefore equally suitable for English-speaking international students and for German-speaking students with very good English skills who are aiming for an international career and who want to use and develop their English language skills intensively in addition to acquiring specialist knowledge.
Information for formerly enrolled students can be found on the website Information for students on older SPSO. Students on older SPSO can be tested upon application under the terms of the current SPSO. The request is irrevocable. Exam and course achievements already achieved are recognized.
Application information for international students
International students: An application is required for this course. Please read the application information.
Label » Starthilfe « – Support when starting your studies (Master)
The »Starthilfe« label stands for support in the transition from Bachelor to Master and in starting your studies in Rostock. The IEF offers these voluntary support offers for all courses of the IEF.
- The Master's degree courses offer new students to Rostock help with starting their studies and settling into Rostock. This includes, in particular, mentoring for freshmen and the information and events offered in the freshers section.
Additional Module offers: JUAS – JOINT UNIVERSITIES ACCELERATOR SCHOOL
JUAS offers two courses in the time from January up to March (each of them for 5 weeks) which are attractive for the students of Electrical Engineering and Computational Science and Engineering. The courses will be accepted for your studies as an elective module on request with 10 ECTS (one course, 5 weeks) or with 20 ECTS (both courses, 10 weeks).
Brief information
Degree
- Master of Science (M.Sc.)
- A successful degree entitles you to use the protected professional title of "Engineer".
Study form
- Continuing (with second professional qualification)
- One-Subject-Master (not combinable with other master courses)
- Full-time and classroom study
Languages
- Lecture language is English, some modules with examination in German.
- The entire study ist possible in English.
- If your native language is not German, a German course is a mandatory component.
Normal duration
- 4 semester / 120 Credit Points
Start
- St winter semester (October 1th) and at Summer semester (April 1th) possible
- Specialization Computational Physics: start at winter semester only
- Specializations Computational Electrical Engineering and Computational Mechanical Engineering: start at winter semester is recommended, start in summer semester possible with limited choices of subjects
Support when starting your studies
- Individual support offers at the start of studies for students who are new to Rostock for their master's degree, including through mentoring by students for students
Fields of study
- Engineering / Electrical Engineering / Mechanical Engineering / Natural Sciences / Physics
Formal requirements
- A first professional qualification in a university degree in Computational Science and Engineering, Electrical Engineering, Information Technology, Mechanical Engineering, Physics, with at least 180 credit points or another equivalent qualification:
- with at least 85 % of the CGPA (Cumulative Grade Point Average) or another grading system with a comparable grade or Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering (GATE) with at least 500 points
- Native language English or proof of sufficient English language skills (proof not older than two years):
- TOEFL IBT with at least 90 points or IELTS with at least 6.5 points
- Solid basic knowledge in mathematics: Good knowledge in linear algebra and calculus (intgral, vector, ...) is required. Knowledge in numerics and stochastics is desireable.
- Solid basic skills in a modern programming language, e.g. C/C++, Fortran, Java, Python, is required. Solid basic knowledge in computer architecture, operating systems and computer networks is desirable. Proof by courses visited in previous studies, certificates from relevant courses, or by working experience mentionned in the CV.
- Proof of profound knowledge:
- for the specialization Computational Electrical Engineering: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves (at least 3 credit points), Mathematics (at least 18 credit points), Programming / Practical Computer Science (at least 6 credit points)
- for the specialization Computational Mechanical Engineering: Mathematics (at least 18 credit points), Technical Mechanics (at least 18 credit points), Thermodynamics (6 credit points), Fluid Mechanics (6 credit points) and Programming (at least 9 credit points)
- for the specialization Computational Physics: Quantum Mechanics (at least 9 credit points), Electrodynamics and Optics (at least 6 credit points), Statistical Physics (at least 6 credit points) and Mathematics (at least 18 credit points)
Application / Enrollment
- German prospective students from the University of Rostock need to be rewritten in the student secretariat of the University of Rostock in this degree program
- German prospective students from other universities must enroll online at the University of Rostock in this program
- International prospective students must:
- apply via UniAssist
- after receipt of the admission letter → then enroll in the study program at the University of Rostock
Specializations
- You have to choose one of this specializations in your application:
- Computational Electrical Engineering
- Computational Mechanical Engineering
- Computational Physics
Further qualification possibilities
- Graduate to Dr.-Ing. or Dr. rer. nat.
Accreditation
- Accredited from: 25.06.2019 to: 30.09.2027
Contakt
1. Introduction - Why studying Computational Science and Engineering?
Computational Science and Engineering is a new, rapidly growing major based on the two traditional disciplines applied mathematics and computer science. The aim of study is the ability of carrying out computer simulations of technical and natural systems from physics, electrical engineering or mechanical engineering based on a sound knowledge of the numerical methods. Numerical simulation provides the capability to enter fields that are inaccessible to traditional experiments and methods of inquiry. As computers become ever faster, the range of application for modeling and simulation is expanding.
Three areas of specialization are offered:
- Computational Electrical Engineering
- Computational Mechanical Engineering
- Computational Physics
2.1 Objectives and features
The aim of the course is to become a Master of Science (M.Sc.) in the field of computational science and engineering.
The Master's degree in Computational Science and Engineering is research-oriented and follows on from the Bachelor's degree.
The language of instruction in the master's program in Computational Science and Engineering is English. It is possible to complete the entire master's program in English. Individual elective modules including module exams are offered in German.
The master's program in Computational Science and Engineering leads to a second professional qualification and enables you to pursue a doctorate.
Successful completion of this course of study entitles you to use the protected professional title of “engineer” in accordance with the Architectural and Engineering Law of the State of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
In this course, you will be given knowledge and skills for a job in academic and industrial fields. On the one hand, you gain the ability to grasp problems in your subject based on mathematical, scientific and engineering knowledge and systematically and purposefully process them scientifically, and on the other hand, after independent training in specific questions, to contribute to development in the field of computational science and engineering. Graduates of the master's program in Computational Science and Engineering are required to have a significantly higher degree of independent, scientific work than graduates of a bachelor's degree, which enables them to participate in the scientific development of their subject and to develop and develop accordingly To be able to carry out research work in industry or in research institutions independently and to be able to take on management tasks.
There are three specializations:
- Computational Electrical Engineering
- Computational Mechanical Engineering
- Computational Physics
For all areas of specialization there are common modules on general methods of applied mathematics and the German language.
2.2 Content requirements
You are well prepared for the start of this course, if you have completed your Bachelor's degree with good results and also have a good knowledge of the English language. In addition you have an special interest in scientific-technical and engineering-based issues and research-based work.
2.3 Special features
The course is offered in English. It is suitable for English speaking international students. It is also suitable for German-speaking students with very good knowledge of English who pursue an international career and in addition to the acquisition and apply of advanced skills of English language.
A semester abroad to deepen the knowledge is possible after the end of the 1st semester.
The level of expertise and academic qualifications of Master of Science comply with the internationally and in Germany well known degree "Diplomingenieur". The various choices in the areas of specialization offered ensure both the scientific depth as well as the relevance of the study for industrial practice.
The Faculty of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering ensures excellent care because of very good student-professor ratio. Further advantages are the proximity to the library, to student dormitories and to the cafeteria.
Students who can only spend about half of the time budget for the study work because of a job or because of family obligations, have the opportunity to apply for the study form Individual part-time studies (Individuelles Teilzeitstudium) twice each for two semesters. Of the two semesters then only one semester will be counted to the standard period of study.
2.4 Fields of activities for graduates
The university master's degree in the field of Computational Science and Engineering offers the best opportunities to get a conductive or research-based engineering job in Germany and over the world. The rapidly increasing demand for engineers and physicists in the fields of electrical and mechanical engineering opens up prospects for the future with good job opportunities and excellent career opportunities. The specializing in the priorities simulation and numerical computing methods will open a ever-growing range of applications.
2.5 Advanced qualification opportunities (PhD)
The master's degree with very good results qualifies to apply for admission for doctoral work (PhD student).
3.1 Structure of the course Computational Science and Engineering (Master)
The studies of the master course Computational Science and Engineering may be commenced in the winter semester or in the summer semester.
Students who choose this master course may specialize in one of this three specializations:
- Computational Electrical Engineering
- Computational Mechanical Engineering
- Computational Physics
The Computational Physics course may only be commenced in the winter semester since the specific obligatory fundamental lecture is not available in summer semesters.
In both courses, Computational Electrical Engineering and Computational Mechanical Engineering, the start of studies is recommended for the winter semester as otherwise there will be only a limited range of modules to select.
Students must select one of these specializations in their application. The mandatory indication of the chosen specialization must be given in written form in the registration for the final examination.
The Master's program is divided into compulsory and elective modules, which are offered in five areas, including the three areas of specialization.
- module list with all modules of this course of study and links to the long descriptions of the modules in the current version (Uni-Web examination portal, language: most in German)
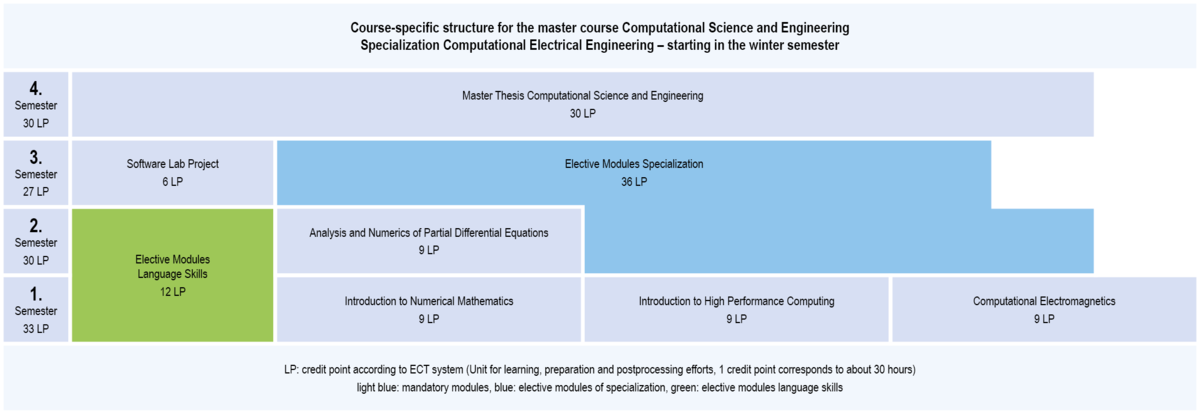
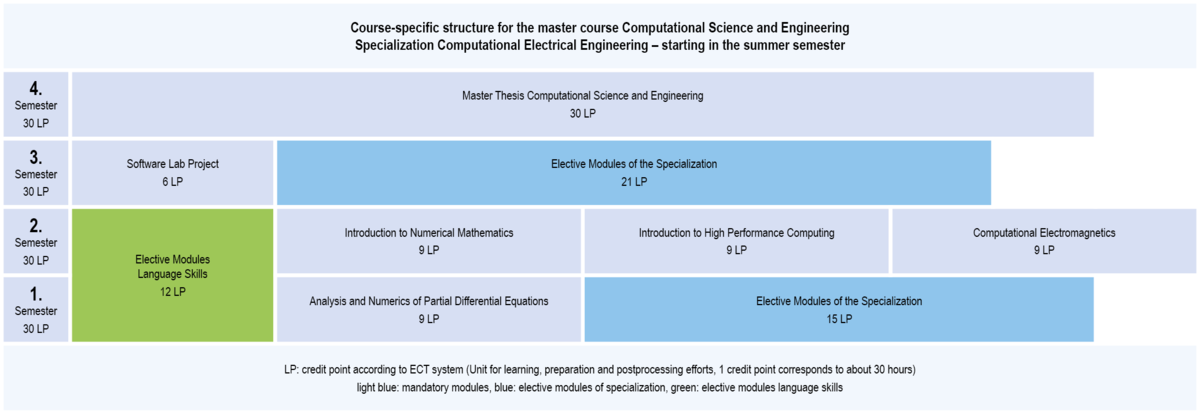
In the specialization Computational Electrical Engineering, compulsory modules with a total of 72 credit points and elective modules in the specialization field with a total of 36 credit points have to be studied.
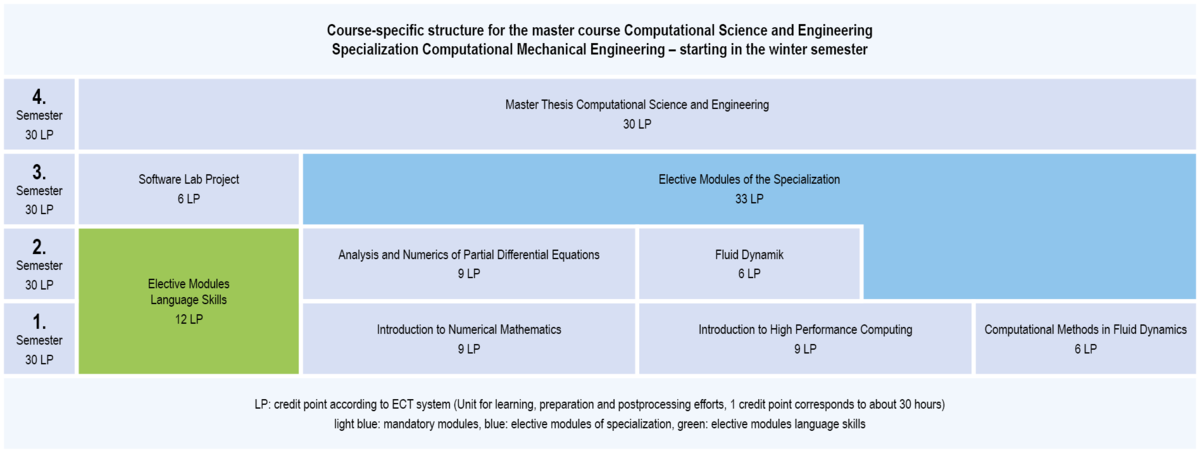
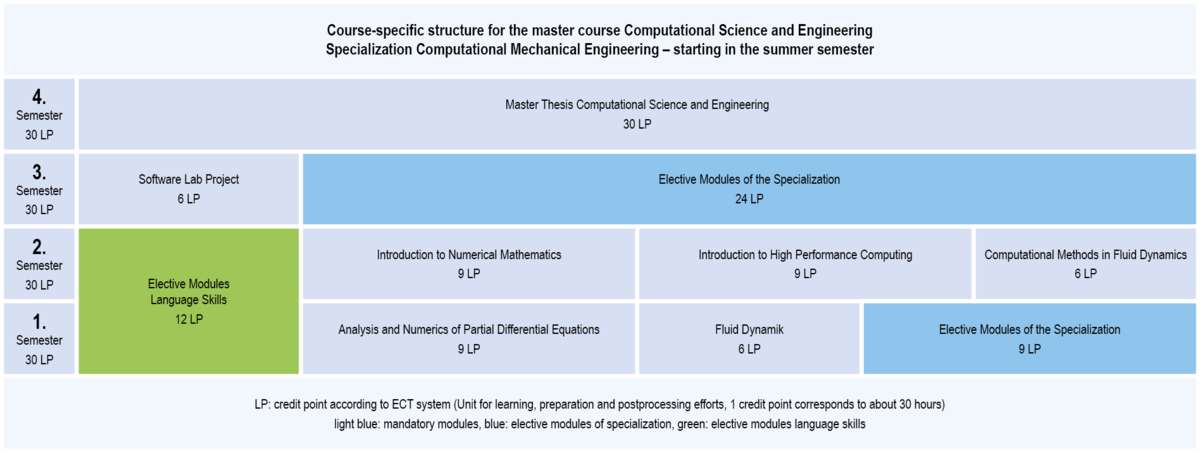
In the specialization Computational Mechanical Engineering, compulsory modules with a total of 75 credit points and elective modules in the specialization field with a total of 33 credit points have to be studied.
In the specialization Computational Physics, compulsory modules with a total of 75 credit points and elective modules in the specialization field of 33 credits have to be studied.
In all three specializations, 12 credits in the compulsory elective language skills have to be studied according to the language center's (Sprachenzentrum) classification. For the language modules, which are studied in the context of the study, the examination regulations apply to the courses offered by the Language Center of the University of Rostock including the university foreign language certificate UNIcert®.
Students with knowledge of German at level B2 of the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages have to attend, after consulting the subject specific student counseling (Fachstudienberatung), modules in the amount of 12 credits from the modules offered by other courses of study at the University of Rostock or other higher education institutions.
In the individual compulsory elective areas of the respective specialization courses, modules amounting to at least 12 credit points from the respective specialization area and a maximum of 12 credit points from the comprehensive elective elective area must be selected.
In all specialization courses, a maximum of 12 credit points can be selected as compulsory elective modules as well as Bachelor modules, provided that they have not already contributed to the passing of the Bachelor's degree.
The final exam has a value of 30 credit points.
At least 120 credits must be earned for passing the Master's examination.
In addition to the compulsory elective modules listed in the SPSO, additional elective modules can be offered. These will be announced locally by the study office before the beginning of the semester.
Participation in individual modules of this program depends on the proof of certain previous knowledge or skills. Details can be found in the respective module descriptions.
3.1.1 Structure of CSE: Specialization Computational Electrical Engineering (start at winter semester)
3.1.2 Structure of CSE: Specialization Computational Electrical Engineering (start at summer semester)
3.1.3 Structure of CSE: Specialization Computational Mechanical Engineering (start at winter semester)
3.1.4 Structure of CSE: Specialization Computational Mechanical Engineering (start at summer semester)
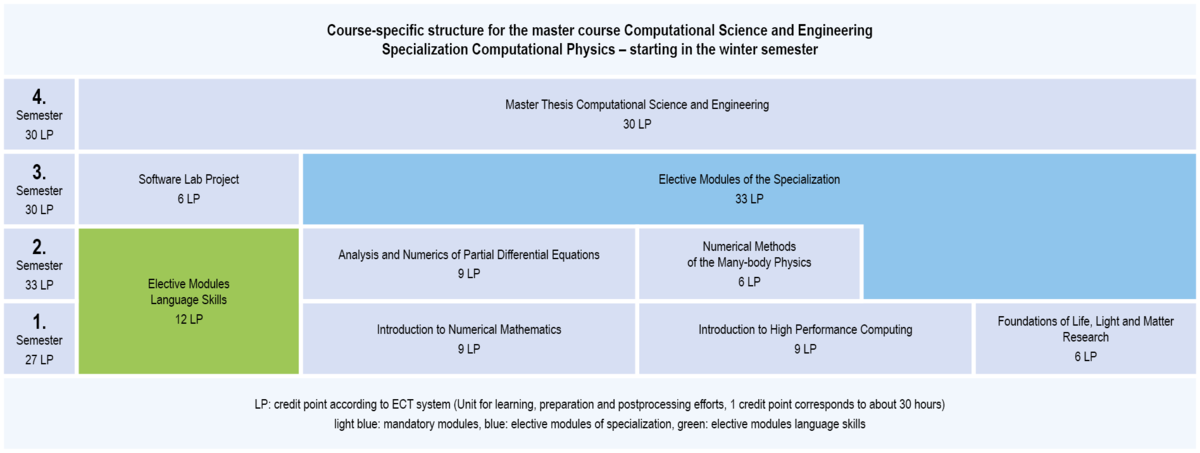
3.1.5 Structure of CSE: Specialization Computational Physics (start only at winter semester possible)
3.2 Module overview
The compulsory modules have to be studied according to the SPSO.
Instead of the elective modules expressly offered for this study program, further modules from the module range of other study programs of the University of Rostock or other universities can be chosen and in accordance with § 19 of the Framework Examination Regulations (Rahmenprüfungsordnung Bachelor / Master), taking into account the qualification objectives of the respective optional subject area in consultation with the subject specific student counseling (Fachstudienberatung) and the corresponding module managers be acknowledged. The examination board (Prüfungsausschuss) decides on the recognition in individual cases. The decision of the examination board should be made at the request of the student before the beginning of the semester in which the module to be recognized should be taken. The attendance of such modules at the University of Rostock presupposes that they are not modules of a restricted admission program, unless a corresponding teaching export is stipulated in terms of capacity law and sufficient study place capacities are available. The admission requirements, examination requirements, examination periods as well as provisions on the form, duration and scope of the module examination, which are provided for in the examination regulations of the respective degree program, apply.
Please note that the courses on offer below are usually only once per academic year - i.e. in the winter semester or in the summer semester. You can obtain information on this from the SPSO or the student office. The division according to SPSO is shown below.
3.2.1 Compulsory modules
Compulsory modules Specialization Computational Electrical Engineering
each semester
- Software Lab Project
- Masterarbeit Computational Science and Engineering (master thesis Computational Science and Engineering)
winter semester
- Introduction to Numerical Mathematics
- Introduction to High Performance Computing
- Computational Electromagnetics
summer semester
- Analysis and Numerics of Partial Differential Equations
Compulsory modules Specialization Computational Mechanical Engineering
each semester
- Software Lab Project
- Masterarbeit Computational Science and Engineering (master thesis Computational Science and Engineering)
winter semester
- Introduction to Numerical Mathematics
- Introduction to High Performance Computing
- Computational Methods in Fluid Dynamics
summer semester
- Analysis and Numerics of Partial Differential Equations
- Fluid Dynamik
Compulsory modules Specialization Computational Physics
each semester
- Software Lab Project
- Masterarbeit Computational Science and Engineering (master thesis Computational Science and Engineering)
winter semester
- Introduction to Numerical Mathematics
- Introduction to High Performance Computing
- Foundations of Life, Light and Matter Research
summer semester
- Analysis and Numerics of Partial Differential Equations
- Numerische Methoden der Vielteilchenphysik (Numerical Methods of many-body Physics)
3.2.2 Elective modules for the respective specialization
According to the specialization, modules from the following offer have to be chosen.
In each specialization, modules amounting to at least 12 credit points (LP) have to be selected from the respective catalogs for the specialization subject.
From the comprehensive compulsory elective catalog modules with a max. 12 credit points are chosen.
Further modules can be selected from the elective catalogs of the other specializations.
The total amount of modules with a Bachelor's level may not exceed 12 credit points.
Selectable mandatory modules of specialization Computational Electrical Engineering
You have to select modules at least with a total of 36 credit points from all lists of selecable mandatory modules. This involves modules at least with a total of 12 credit points from this list:
winter semester
- Advanced VLSI Design
- Akustische Sensorik (Acoustic Sensors)
- Bild-/Videoverarbeitung und Codierung (Image / Video Processing and Encoding)
- C++ / GUI
- Computational Intelligence in Automation
- Fehlerdiagnose und Fehlertoleranz in technischen Systemen (Fault Diagnosis and Fault Tolerance in technical Systems)
- Modeling and Simulation of Mechatronic Systems
- Photonische Systeme (Photonic Systems)
- Sensors and Actuators
summer semester
- Advanced Computational Electromagnetics and Multiphysics
- Advanced Electromagnetic Simulation and Multiphysics
- Biosystems Modeling and Simulation
- Compact Modeling of Large Scale Dynamical Systems
- Hochintegrierte Systeme (Highly integrated Systems)
- Nature-Inspired Computing
- Programmierbare integrierte Schaltungen (Programmable integrated Circuits)
Offer irregular
- Theory and Application of Fast Algorithms for Acoustic and Electromagnetic Problems (added on 08.02.2021)
Selectable mandatory modules of specialization Computational Mechanical Engineering
You have to select modules at least with a total of 33 credit points from all lists of selecable mandatory modules. This involves modules at least with a total of 12 credit points from this list:
winter semester
- Information Technology in Ship Design and Production
- Mathematische Modelle in der Schiffstheorie (Mathematical Models in Ship Theory)
summer semester
- Modellierung und Simulation der Turbulenz (Modeling and Simulation of Turbulence)
- Nature-Inspired Computing
Selectable mandatory modules of specialization Computational Physics
You have to select modules at least with a total of 33 credit points from all lists of selecable mandatory modules. This involves modules at least with a total of 12 credit points from this list:
winter semester
- Atoms and Clusters
- Dynamik der Atmosphäre (Dynamics of the Atmosphere)
- Einführung in die Atmosphärenphysik und in die Physik des Ozeans (Introduction to Atmospheric Physics and Ocean Physics)
- Fundamentals of Photonics
- Molecular Physics
- Physik der Ionosphäre (Physics of the Ionosphere)
- Prozesse im Küstenozean (Coastal Ocean Processes)
- Simulation Methods of Molecular Biophysics
summer semester
- Grundlagen der Quantenoptik (Fundamentals of Quantum Optics)
- Marine Turbulenz (Marine Turbulence)
- Nonlinear Optics and Spectroscopy
- Ozeanmodellierung (Ocean Modeling)
- Physik des Klimas (Physics of Climate)
- Plasma- und Astrophysik (Plasma Physics and Astrophysics)
- Quantenoptik (Quantum Optics)
- Spezielle Themen aus der Atmosphärenphysik (Specific Topics of Atmospheric Physics)
- Theoretische Ozeanographie (Theoretical Oceanography)
- Weiterführende Konzepte der Atmosphärenphysik (Advanced Concepts of Atmospheric Physics)
3.2.3 Overarching selectable mandatory modules for all specializations (at most 12 credit points)
You have to select from this catalog modules with a maximum of 12 credit points.
winter semester
- Computer Vision
- Datenbanken für Anwender (Data Bases for Users)
- Mathematik für Wirtschaftsinformatik 3 (Mathematics for Business Information Systems 3)
- Modellierung und Simulation von kontinuierlichen und hybriden Systemen (Continuous and Hybrid Systems Modeling and Simulation)
- Numerische Behandlung gewöhnlicher Differentialgleichungen (Numerical Analysis of Ordinary Differential Equations)
- Scalable Computing
summer semester
- Beschleunigertechnologie und Strahldiagnose (Accelerator Technology and Beam Diagnostics)
- Numerische Behandlung partieller Differentialgleichungen (Numerical Analysis of Partial Differential Equations)
- Virtual Reality
3.2.4 Compulsory Elective Area Languages (at most 12 credit points)
You have to visit two modules according to the classification of the Language Center (Sprachenzentrum).
each semester
- Deutsch A1.1 GER
- Deutsch A1.2 GER
- Deutsch A2.1 GER
- Deutsch A2.2 GER
- Deutsch B1.1 GER
Students with knowledge of German at level B2 of the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages have to attend, in consultation with the subject specific study counseling (Fachstudienberatung), modules in the amount of 12 credit points from the modules offered by other courses offered by the University of Rostock or other universities.
Of course you are free to attend additionally any lecture of the University of Rostock. You can obtain credit points by this courses. For counting of these credit points up to your studies or list this lectures additionally at your masters certificate please ask the students office before. Normally it is necessary to submit an application. The University of Rostock offers a broad spectrum of subjects and lectures. You will have interesting opportunities to get additional knowledge and skills.
3.3.1 Time schedule
The examination and study plan forms the basis for the respective semester study plans, which are made available to the students in the usual way.
3.3.2 Teaching and training forms
The studies’ contents are taught in different classes. The different kinds of classes are signified by the practice of different forms of teaching and learning. Usually, classes are offered only once a year.
The following kinds of classes are deployed in the master course:
- Excursion: Excursions are courses that take place in a non-university environment. These include, for example, study trips or field internships, which are carried out for technical reasons in practice-oriented environments or at external study-relevant locations.
- Consultation (to supervise scientific work): Consultations are individual counseling sessions between students and teachers. The students produce long-term scientific studies or thesis. The teacher will inform himself at regular intervals about the status of the work and give suggestions.
- Internship event: An internship event is an internship at the university, which, unlike non-university internships, is a supervised course. It is an exercise to apply acquired theoretical knowledge to specific practical issues, to practice scientific methods and techniques by practical application and to deepen the contents of the module and to train their own work organization.
- Practical school practice: In a practical school exercise, students teach under instruction individual lessons at a school facility.
- Seminar: In a seminar, the students will have the opportunity to present their own findings, to put them up for discussion and to present them in written form. Seminars can be conducted as a presence or online event.
- Tutorial: A tutorial is a course that is carried out by academic or student assistants to supplement a course in accordance with a study regulations. The responsibility for the technical and didactic care lies with the institution or the scientific or artistic staff to which the assistant is assigned.
- Exercise: In an exercise that is not predominantly practical in nature, the students work on given exercises to deepen and apply the knowledge and the imparting of subject-specific skills and abilities. An exercise offers the opportunity to ask questions, to discuss solutions to problems and to use means of self-control of the achieved level of knowledge.
- Lecture, Repetition: In a lecture or a repetition, the students will be presented with the curriculum primarily as a lecture of the teacher with the support of media (panels, slides, scripts). Lectures or repetitions can be carried out as a presence or online event.
- Integrated course: An integrated course combines the lecture with more active forms (eg seminar or exercise) in which the students themselves elaborate given topics on the basis of literature and represent them in the circle of the participants of the event and can discuss.
- Project event: In the project event, students work on a project topic in individual or group work under supervision of a lecturer.
The achievement of the aims of study is dependent on the participation in classes as well as the accompanying self-study.
3.3.3 Mandatory attendance
If specified in the module descriptions, exercises, seminars and internships require compulsory attendance according to § 6b of the Framework Examination Regulations (Rahmenprüfungsordnung Bachelor / Master):
- For courses where regular or active participation of the candidates in the course is required to achieve the learning objective, compulsory attendance may be compulsory, provided specific techniques, didactics, knowledge and skills are taught in the specific course in pure self-study can not be learned or only with considerable restrictions. The corresponding types of events are specified in the study program-specific examination and study regulations (SPSO) and must be identified as such in the respective module description. The requirement of regular attendance is deemed met if no more than 20 percent of the sessions of the course were missed without excuse. Also during the study excursions can be carried out, in which to achieve the learning objective is to participate. If the requirement of regular participation is not fulfilled, no admission to the module examination takes place.
- Absence is always to be excused before the start of the event or the excursion, stating the reason (usually by e-mail); If this is not possible in individual cases, the apology must be made immediately afterwards. If the lecturer does not find a valid reason for not attending, the absence is considered as unjustified.
- Can the candidate make a written statement and make it convincing that for reasons beyond his control (eg own illness, care for a sick or otherwise needy close relative, pregnancy, death of a close relative) have come to longer absences the lecturer decides whether the actual participation time can still be counted as regular participation. The same applies if it was not possible to take part in an excursion or only partially. With regard to the absence of time, the provision of an adequate equivalence performance can be specified. The nature of this compensatory benefit will be determined by the instructor at its sole discretion. The time required to provide them may not exceed twice the duration of the missed teaching time.
- If the requirement of regular participation is not met by the candidate and no equivalence service can be provided, this must be reported in writing by the lecturer, stating the reasons, to the examination board (Prüfungsausschuss). The latter issues a decision, which must be provided with a legal remedy. Against the decision, the objection to the examination board is admissible.
3.4 Examinations
The composition of the modules to be attended, the type of examinations, the type, duration and scope of the module examinations, the regular exam date and the credit points to be achieved follow from the examination and study plan and the module descriptions. The final exam (master thesis and colloquium) is part of the Master's examination.
In particular, the following examinations are used:
written examinations
- Report / Documentation: A report (also documentation) is a factual representation of an event or the structured presentation of facts. A report can be in the form of a portfolio. A portfolio is an orderly collection of written documents or own works. Examples of reports are: internship documentation, interviews, research reports, journalistic articles and literature reports.
- Essay: An essay is a short essay in which a limited topic is discussed in an over-the-topical and informal way. It is more about the development of a guiding idea or a preliminary idea than the stringent presentation of complex content. The essay must satisfy the substantive objectivity and identify sources of quotes or suggestions.
- Homework: A homework is a written elaboration on a given topic or the written processing of a task. Students should be able to demonstrate that they can tap sources of literature within a limited space of time, that they can present reflected texts in their own words in an independent context of argumentation and that they can independently and completely work on tasks. Possible special forms of a term paper may in particular be a case study / case analysis, a lesson draft / lesson design, a research exposition or a design draft. In addition to the housework, a presentation of the topic may be required.
- Exam: In an exam, the students have to work under written supervision in a given time without or with limited resources.
- Protocol: A protocol is an accurate, essentially transcript of the course of an investigation, an experiment or the course of an event.
oral examinations
- Colloquium: Questions will be asked by a knowledgeable auditorium following a presentation of the student's own work.
- Oral examination: In an oral examination, students should answer questions on one or more examination topics orally.
- Presentation: A presentation is a presentation on a scientific topic and summarizes the research results, the results of the study and / or the results of a literature study. With the help of a sensible use of media essential contents of the used literature should be briefly presented, explained and questions formulated for further discussion. In addition to the presentation, a handout, a thesis paper or a written version of the presentation may be required.
practical examinations
- Practical Examination: In a practical examination, students should demonstrate competences for performing professional or professional activities or their own practical, sporting or artistic abilities. Possible forms of practical exams include: school practice exam, bedside exam, role play, simulation game, moot court, sports exam, music exam.
- Project work: The project work is an open type of examination with a high degree of freedom. Project work should be done individually or by several students within one semester. The basis for the examination is both the result of the project work as well as its documentation and the process of the group work itself. The results of the work can, for example, be presented in a portfolio.
Within one module, study achievements may be a prerequisite for the module examination. The prerequisites may be evaluated and graded but may not affect the final module grade.
Prerequisites can be:
- presentations
- project reports
- Exercise certificate / Exercises: The solution of exercises serves to test the performance level of the students even during the lecture period and usually takes place without supervision.
- Control Work / Document Work: are written elaborations of the solution of given tasks. They also serve to test the performance level of the students during the lecture period. Inspection work must be carried out under supervision of the instructor at a specified location.
- Programming projects: are project work in which the students show that they have understood the subject matter and can apply it creatively. For this they independently carry out programming work, which will be presented and evaluated in the course of the event in accordance with the instructor.
- Simulation projects: are project works in which the students show that they have understood the subject matter and can apply it creatively. For this they independently carry out work, which will be presented and evaluated in the course of the event in accordance with the teacher's instructions.
Specific prerequisites can be referenced in the respective module descriptions as well as the examination and study plan.
The course-related module examinations will be taken during the specified examination period. The examination period of a semester begins immediately after the lecture period and ends at the end of the semester.
By way of derogation, the module examinations in the form of abstracts, presentations, reports and project work may be taken during the course of the event if the students are informed at the latest in the first lecture week about the type of examination applicable to them, their scope and the respective deadline. In agreement between students and examiners, examinations may be held at other times, subject to the deadlines and application modalities specified in the framework examination regulations (Rahmenprüfungsordnung Bachelor / Master).
The declaration of withdrawal of the application for module examinations must be made in writing to the student office. The same applies to the application for the evaluation of a module examination as a free test.
In the case of the last examination attempt, the examiner decides whether an oral examination should be carried out in deviation to the form of examination specified in the module handbook. This selection must be made uniform for all students of a semester.
In the case of a change in a module description, repeat examinations must be taken in accordance with the module description in the version that applied to the examination to be repeated.
3.5 Study abroad
As part of the compulsory elective course, as from the second semester, as an alternative to the examination and study plan, the Master's program gives students the opportunity to complete a maximum of one semester at a foreign university.
The stay abroad must be prepared early. For this purpose, the student first chooses a thematic focus corresponding to the main research areas of the faculties participating in the degree program and usually seeks contact during the course of the semester with the Study Advisory Board, the Examination Board and in addition to the Rostock International House. The study counseling arranges research partners and helps to organize the semester abroad. A list of research partners is maintained.
The stay abroad must be independently organized and financed by the student.
Competences acquired at the foreign study site are recognized, provided that there are no significant differences to the competences to be acquired within the framework of the Master's Program Computational Science and Engineering. To secure recognition, the students and the chairperson of the examination board conclude a teaching and learning agreement in accordance with § 5 (3) of the framework examination regulations (Rahmenprüfungsordnung Bachelor / Master) before taking up residence abroad.
3.6 Individual part-time study
The student may declare to the Examination Board (Prüfungsausschuss) no later than two weeks before the beginning of a semester that in the following two semesters, he / she will only receive approximately the amount of work due to his or her work or family responsibilities in education, care and nursing Half of the working time for her / his studies. The application must specify which of the intended modules or module parts are not provided and in which subsequent semesters the corresponding offered modules or module parts are to be made up. If the examination committee approves the application, it may provide for the retrofitting of modules or module parts other than those specified in the application, in particular if this is necessary to ensure proper study. In hardship cases, the application can also be made at a later date.
The application must be sent to the examination board (Prüfungsausschuss) and submitted to the study office (Studienbüro). If the decision differs from the application, the student is to be heard in advance. The application can be withdrawn up to two months after the start of the semester.
In the case of approval, one semester is not counted towards the standard period of study and, accordingly, is disregarded in the calculation of the periods specified in § 9 and § 10 of the Framework Examination Regulations (Rahmenprüfungsordnung Bachelor / Master). During part-time studies, examinations other than those specified in the decision of the Examination Board can not be effectively taken; a double study during this time is inadmissible. Otherwise, the rights and obligations of the students concerned remain unaffected.
Each student can use the scheme a maximum of two times.
4.1 Entry requirements
As a prerequisite for entry to the Master's degree program, a first professional qualifying university degree is required. In addition, the program specific examination and study regulations (SPSO) may specify further admission requirements (for example, professional qualifications and language skills).
further information:
- entry requirements (Uni-Web)
- entry requirements for master courses (Uni-Web)
- entry and admission requirements for international students (Uni-Web)
4.1.1 First professional qualification
- a first professional qualification in computational science and engineering, electrical engineering, information technology, mechanical engineering, physics with at least 180 credit points or another equivalent qualification
- degree with at least 85 % of the CGPA (Cumulative Grade Point Average) or with a different grading system with a comparable grade or Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering (GATE) with at least 500 points
4.1.2 Further entry requirements
The following additional entry requirements apply to this degree program:
- Applicants whose native language is not English must have a TOEFL IBT of at least 90 points or an IELTS of at least 6.5 points to prove their English language skills. The proof must not be older than two years.
- Evidence of in-depth knowledge of the following subject areas must be provided:
- for the specialization Computational Electrical Engineering: electromagnetic fields and waves (at least 3 credit points), mathematics (at least 18 credit points), programming / practical computer science (at least 6 credit points)
- for the specialization computational mechanical engineering: mathematics (at least 18 credit points), engineering mechanics (at least 18 credit points), thermodynamics (6 credit points), fluid mechanics (6 credit points) and programming (at least 9 credit points)
- for the specialization computational physics: quantum mechanics (at least 9 credit points), electrodynamics and optics (at least 6 credit points), statistical physics (at least 6 credit points) and mathematics (at least 18 credit points)
4.2 Application / Enrollment / Description
This degree program is not restricted to admission (no numerus clausus).
- Prospective students of the University of Rostock need only describe themselves (see 4.2.1.).
- Prospective students from Germany only have to enroll (see 4.2.2).
- International prospective students must apply and then enroll on receipt of the admission notice (see 4.2.3).
4.2.1 Prospective students from the University of Rostock
An application is not required.
Enrollment takes place online in the registration portal of the University of Rostock:
- from August 1st to September 30th for the next winter semester or
- from February 1st to March 31st for the next summer semester
further information:
- enrollment for masters courses (including description form) (Uni-Web)
4.2.2 Prospective students from Germany
An application is not required.
Enrollment is online in the enrollment portal of the University of Rostock:
- from the 1st of August to the 30st of September for the next winter semester or
- from the 1st of February to the 31st of March for the next summer semester
further information:
- enrollment for masters courses (Uni-Web)
Please also note the information on the application.
International prospective students must be in the period
- from the 1st of April to the 31th of May for the next winter semester or
- from the 1st of October to the 30th of November for the next summer semester
apply online at UniAssist and then enroll in the degree program at the University of Rostock upon receipt of the admission letter. More information can be found on the Website of the University of Rostock below.
further information:
5.2 Videos
- Study at the IEF (Video on YouTube)
Please note: As soon as you watch the video, information about it will be sent to YouTube / Google. For more information, see Google Privacy.
5.3 Regulations
- Degree-specific examination and study regulations Master Computational Science and Engineering (SPSO MSc CSE 2018) / Studiengangsspezifische Prüfungs- und Studienordnung Master Computational Science and Engineering (SPSO MSc CSE 2018) (please notice: this document in German language is the binding official document)
Student advisory service Computational Science and Engineering / Studienfachberatung Computational Science and Engineering
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Dennis Hohlfeld
Albert-Einstein-Straße 2 (seminar building / Seminargebäude, room / Raum 016), 18059 Rostock, GERMANY
fon: +49 (0)381 - 498 7004
cse.ief(at)uni-rostock.de
Study Office and Examination Office Computational Science and Engineering / Studienbüro und Prüfungsamt Computational Science and Engineering
Anita Björk-Pagel
Albert-Einstein-Straße 26, 18059 Rostock, GERMANY
Room / Raum 006
Tel.: +49 (0)381 - 498 7004
cse.ief(at)uni-rostock.de
Examination Board Computational Science and Engineering (chair) / Prüfungsausschuss Computational Science and Engineering (Vorsitz)
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Dennis Hohlfeld
Albert-Einstein-Straße 2 (seminar building / Seminargebäude, room / Raum 016), 18059 Rostock, GERMANY
fon: +49 (0)381 - 498 7004
cse.ief(at)uni-rostock.de
Student representation Computational Science and Engineering / Studierendenvertretung Computational Science and Engineering
Student Council Electrical Engineering / Fachschaftsrat Elektrotechnik
room of the Student Council / Fachschaftsraum: room / Raum 003 and / und 004, Albert-Einstein-Straße 26, 18059 Rostock, GERMANY
Student Project Room: semnar building / Seminargebäude, lab / Labor S 13, Albert-Einstein-Straße 2, 18059 Rostock, GERMANY
fachschaft.e-technik(at)uni-rostock.de
Student Service Center (SSC) of the University of Rostock / Student Service Center (SSC) der Universität Rostock
Info service in the SSC: Central contact point for prospective students and students
The Student Service Center brings together all the important information and advice offered by various institutions for prospective students and students. Those seeking advice should first contact the info service. If necessary, referrals are made here or an individual consultation appointment is arranged.
Parkstraße 6, 18057 Rostock, GERMANY, room / Raum 024
fon: +49 (0)381 - 498 1230
studium(at)uni-rostock.de
contact and office gours: Student Service Center (SSC) of the University of Rostock – Homepage
On the SSC homepage you will find information on which institution is represented at which times in the SSC.
General Student Advisory Service & Careers Service / Allgemeine Studienberatung & Careers Service
General Student Advisory Service of the University of Rostock / Allgemeine Studienberatung der Universität Rostock
Brief advice on choice of course, reorientation and course of study
Parkstraße 6, 18057 Rostock, GERMANY, room / Raum 024
fon: +49 (0)381 - 498 1234 and +49 (0)381 - 498 1230
studium(at)uni-rostock.de
contact and office hours: General Student Advisory Service
Student's office / Studierendensekretariat
Student's Office of the University of Rostock / Studierendensekretariat der Universität Rostock
Contact point for questions about admission, registration and re-registration
Parkstraße 6, 18057 Rostock, GERMANY, room / Raum 024
fon: +49 (0)381 - 498 1230
studierendensekretariat(at)uni-rostock.de
contact and office hours: Student-Service-Center
Rostock International House (RIH)
Rostock International House (RIH) of the University of Rostock
Point of contact for questions about study visits abroad (outgoing), studying in Rostock for international students (incoming) and prospective refugees (refugees)
Kröpeliner Straße 29, 18055 Rostock, GERMANY
fon: office: +49 (0)381 - 498 1209 and +49 (0)381 - 498 1700
info.rih(at)uni-rostock.de
contact and office hours: Rostock International House (RIH) – Contact and opening times